
 English
English  Español
Español Português
Português русский
русский Français
Français 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Polski
Polski 한국어
한국어 Svenska
Svenska magyar
magyar Malay
Malay বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার Dansk
Dansk Suomi
Suomi हिन्दी
हिन्दी Pilipino
Pilipino Türkçe
Türkçe Gaeilge
Gaeilge العربية
العربية Indonesia
Indonesia Norsk
Norsk تمل
تمل český
český ελληνικά
ελληνικά український
український Javanese
Javanese فارسی
فارسی தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు नेपाली
नेपाली Burmese
Burmese български
български ລາວ
ລາວ Latine
Latine Қазақша
Қазақша Euskal
Euskal Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk Македонски
Македонски Lietuvos
Lietuvos Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel Română
Română Slovenski
Slovenski
How Does PCB Cloning Differ from PCB Reverse Engineering?
2025-02-22
In the world of electronics, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are crucial for the functionality of various devices. When there is a need to replicate, analyze, or improve an existing PCB, two common methods come into play: PCB cloning and PCB reverse engineering. While they may seem similar, they serve different purposes and involve distinct processes. Understanding the differences between these two techniques can help determine which approach is best suited for a particular project.
What is PCB Cloning?
PCB cloning is the process of duplicating an existing PCB without making any modifications. This method is often used when the original design files, such as schematics and Gerber files, are unavailable but a working replica of the board is needed.
The cloning process begins by analyzing the physical PCB, scanning its layers, and extracting the layout and circuit traces. Advanced software tools help replicate the PCB’s design, including the placement of electronic components and copper traces. Once the data is gathered, a new board is manufactured to be an exact copy of the original.
PCB cloning is commonly used for replacing obsolete or discontinued PCBs, producing identical copies for large-scale manufacturing, and recovering lost designs. Since this method focuses on replication rather than redesign, it does not involve any performance enhancements or circuit modifications.
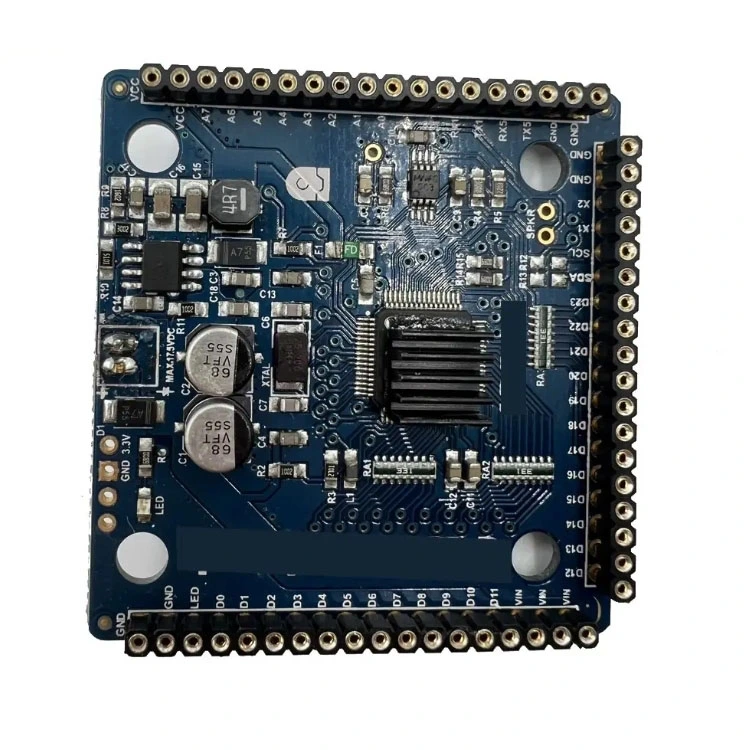
What is PCB Reverse Engineering?
PCB reverse engineering is a more detailed and analytical approach that involves studying the PCB’s design to understand how it functions. This technique is often used to troubleshoot issues, improve existing designs, or recreate schematics for a PCB that lacks documentation.
Unlike cloning, reverse engineering does not simply copy the PCB; instead, it breaks down the circuit design, traces signal paths, and identifies how components interact. Engineers may disassemble the board layer by layer, map out connections, and reconstruct the original schematics. This process allows for modifications, such as replacing outdated components, optimizing the circuit for better performance, or redesigning the board for specific improvements.
PCB reverse engineering is widely used in product development, failure analysis, research and development, and upgrading old electronic systems. It is an essential tool for engineers looking to enhance or modify an existing PCB rather than just duplicating it.
Key Differences Between PCB Cloning and PCB Reverse Engineering
The fundamental difference between PCB cloning and PCB reverse engineering lies in their purpose and complexity. Cloning focuses on making an exact duplicate without changes, while reverse engineering involves detailed analysis and possible modifications to the design.
PCB cloning is ideal when the goal is to reproduce an existing board as it is, whether for manufacturing, repair, or replacing outdated components. In contrast, reverse engineering is the preferred approach when improvements, troubleshooting, or design recovery are needed.
While both techniques are valuable in electronics, choosing the right method depends on the specific needs of the project. If you need an exact replica, PCB cloning is the way to go. If you need insights into the design and potential improvements, PCB reverse engineering is the better option.
In the field of PCB Clone, Greeting, as a leader, has always been imitated but never surpassed. The company combines the latest EDA design software, professional copying technicians and advanced process technology to clone single-layer, double-layer, multi-layer (up to 48 layers) PCB circuit boards, and can copy various high-difficulty PCB circuit boards such as blind and buried holes.Visit our website at www.grtpcba.com to learn more about our products. For inquiries, you can reach us at sales666@grtpcba.com.




